Share to:
Related Products
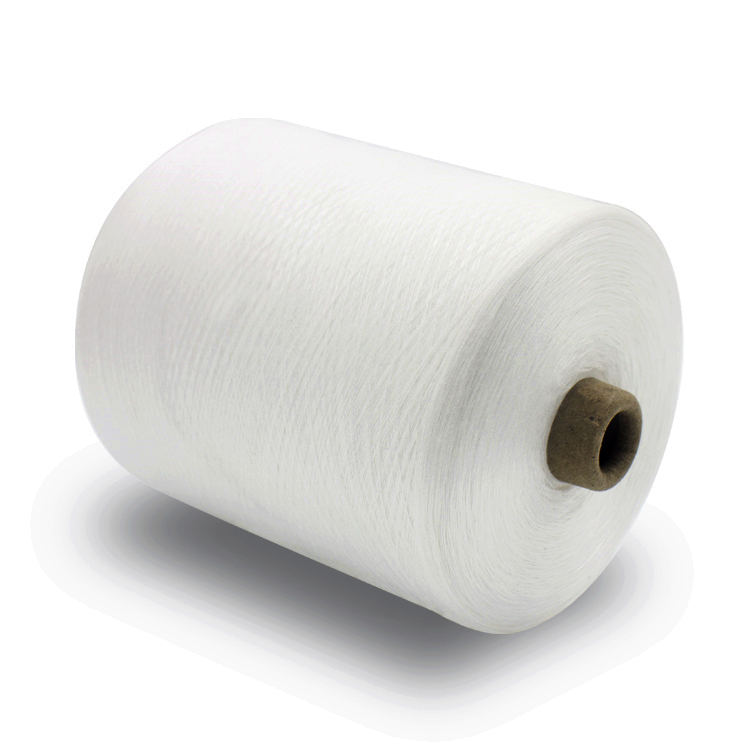
Multi-color cotton monofilament yarn for textile dress
LQ-0404
Price: From $0.66
Delivery time: 9-20 days after payment
MOQ: 500 KG
Material:100% cotton
Pattern:Raw
Yarn type:Filament
Feature:Eco-friendly, high tenacity
Yarn count:50D-300D
Strength:2.24
Place of origin:Guangzhou
Use:Knitting, sewing, weaving
Usage:Knitted fabric,woven fabric
Certificate:Oeko-tex standard 100,OEKO, ISO9001, SGS,Global Recycled Standard
| Material | 100% Cotton Yarn | Certification | Oeko-Tex Standard 100,ISO90012008, ISO140012004 |
| Technics | Ring Spun | Colors | Black,White,Colors |
| Feature | Eco-Friendly, Anti-Bacteria, Moisture-Absorbent, Anti-Pilling, Colour fastness grade 3-4 | Type | Pure cotton yarn |
| Use | Sewing, Hand Knitting, Knitting, Weaving, Embroidery | Packing | PP weaving bags and Cartons |
| Twist | 800 -1100tpm | Application | Socks, Towels, Tablecloths, Carpets, Knitwear, Ribbon. |
| Evenness | 15 | Sample days | Within 1-7 days after payment |
| Yarn Count | 21,32,40 | Yarn Type | Combed |
| Strength | 220-450 | Pattern | Raw |
| More specifications can be customized | |||
1. Overview of Cotton textile yarn
Cotton textile yarn is a kind of yarn made of cotton fibers by spinning process. It is called cotton yarn after processing by stock. According to different spinning processes, it can be divided into carding yarn and combing yarn.
(1) Carding textile yarn: It is a yarn made of cotton fibers through ordinary spinning system.
(2) Combed textile yarn:This yarn made of cotton fibers through combed spinning system.
Combed textile yarn is made of high quality raw materials. In the yarn, the fibers are straight and parallel, the knots are few, the luster is good, the yarn is even and the strength is high. This kind of cotton yarn is mostly used for weaving high-grade fabrics.

2. Processing
Cotton yarn production and manufacturing methods are relatively complex. Generally speaking, there are two kinds of spinning methods, namely carding spinning and combing spinning.
(1) Carding spinning process: cotton blending opening and cleaning carding drawing roving spinning post-processing finished product inspection.
(2) Combed spinning process: cotton blending opening and cleaning carding combing drawing roving spinning post-processing finished product inspection.
3. Use
Cotton yarn is widely used. It can be used as woven yarn or knitting yarn. Especially combed yarn can be used to produce textiles with high quality requirements, such as high-grade sweaters, fine poplin, etc. Cotton yarn can also produce special industrial yellow wax cloth, tire cord cloth, high-speed sewing thread and embroidery thread.

4. Origin and country of export
(1) Cotton yarn has a long history of production and export in China and occupies a certain position in foreign trade. At present, all provinces, cities and regions have the capacity of cotton yarn production and export, and the larger output and export volume are Shanghai, Tianjin, Beijing, Qingdao, Xi'an, Shijiazhuang, Handan, Henan, Sichuan, Hubei and other provinces and cities.
(2) The main export targets are Europe, the United States, Japan, Hong Kong and Macao and other countries and regions.
5. Cotton textile yarn types
There are many kinds of cotton yarn classification methods.
(1) According to business habits:
1.The cotton yarns below tex are all roving yarns. Mainly used for weaving thick or looped cotton fabrics, such as coarse cloth, velvet, strong cloth, etc.;
2. Middle count yarn: 18-27 cotton yarns are middle count yarns, used for weaving plain cloth, twill cloth, satin and other general fabrics;
3. Spinning yarn: 28 or more cotton yarns, used for weaving fine cloth poplin, high-grade needles, woven fabrics.
(2) According to the spinning method:
Carded yarn: ring spinning yarn without combing process, used for general needle and woven fabrics; combed yarn: using high-quality cotton fibers as raw materials, adding a combing process to the combed yarn in spinning, and spinning yarn of good quality, used for weaving high-grade fabrics, such as high-grade poplin, fine cloth, etc. (3) Waste spinning: refers to the yarn made entirely from waste cotton treated in the spinning process, which is used to weave low-grade cotton blankets, flannel cloth and wrapping cloth; and (4) new spinning: yarn made from a new spinning system.
(3) According to twist direction:
Backhand twist (also known as Z twist) yarn is the most widely used in various fabrics. Backhand twist (also known as S twist) yarn is used for weft weaving of wool cloth.
(4) According to yarn use:
Warp yarn is the yarn parallel to the warp edge in woven fabrics, which has greater strength and larger twist in general; weft yarn is the yarn perpendicular to the warp edge in woven fabrics, which requires lower strength and lower twist than warp yarn to maintain a certain degree of softness; and knitting yarn requires cleanliness, uniformity and smaller twist in order to prevent it. Broken ends are caused when knitting is bent; Industrial yarns such as tyre cord, conveyor belt yarn, medical yarn, etc.
(5) According to yarn dyeing and finishing and post-processing points:
1) Natural yarn (also known as primary color yarn): maintain the natural color of fibers for weaving primary color grey cloth;
2) dyed yarn: primary color yarn cooked and dyed for dyeing and weaving;
3) dyed yarn (including blended yarn): yarn dyed with fibers first, then spun, can be woven into fabrics with irregular stars and patterns;
4) bleaching yarn: Bleached with primary yarn, used for weaving bleached cloth, can also be interwoven with dyed yarn into various dyed products; Mercerized yarn: mercerized cotton yarn. There are mercerized bleaching and mercerized dyeing yarns for weaving high-grade dyed fabrics; _Sintering yarn: Sintering machine burns off the yarn surface hairs to produce yarns with smooth surface for weaving high-grade products.

Specification and quality:
(1) Specification and quality of cotton yarn:
There are 70-56, 55-44, 43-37, 36-29, 28-19, 18-17, 16-10, 9-7, 6-3 single yarn specifications for carding cotton. There are 150-131, 130-111, 110-91, 90-71, 70-56, 55-44, 43-37, 36-29, 28-19, 18-16 single yarn specifications for combed cotton.
Knitting yarn requires small twist, even yarn, to ensure that knitted cashmere is thick, elastic and warm. Weaving yarns require light weight, less weft knots and evenness.
(2) Inspection method: According to national standards, yarn quality is evaluated according to quality index and weight unevenness. Cotton yarn is graded according to evenness, neps and number of impurities. The quality index mainly refers to the strength of yarn, which reflects the wear resistance and durability of fabric to a certain extent. The grade of yarn mainly reflects the difference of yarn thickness and appearance defects. It directly affects the appearance of fabric, such as the uniformity of grain, clarity and the size of shadow. Yarn quality is closely related to production management, process conditions, mechanical condition, technical operation level, the quality of raw cotton and its rational use.
The technical index of cotton textile yarn can be found in GB/T398-93 national standard.
Cotton yarn inspection methods are as follows: GB/T398-93 Cotton natural colored yarn; GB/T4743-95 Yarn Density (or Number of Yarns) Measurement Method-Skeing Method; SN/T0450-95 Export Natural Colored Cotton Yarn and Combed Polyester Cotton Blended Yarn Inspection Rules.
Inspection shall be carried out in accordance with the quality specifications and indicators stipulated in the trade contract.
Packaging, storage and transportation
Cotton yarn can be divided into bobbin yarn and skein yarn according to different moulding purposes.
The inner packing of cotton yarn is a plastic bag with labels of factory name, product name and specifications, registered trademark name, grade, weight, batch number, package number, quantity of yarn and package date.
Cotton yarn is mainly packaged in cartons or plastic woven bags. The packing should be neat, dry and strong, suitable for long-distance transportation.
The validity period of cotton yarn inspection is one year in the north and half a year in the south. Those exceeding the validity period must be inspected. Check the main items: mildew, moth, water, pollution, damage and so on.
Processing and ordering matters needing attention
Because of the different origin and batch number of cotton, the performance of cotton varies greatly. Therefore, different batches of cotton should be rationally mixed in processing. When signing the contract, attention should be paid to the clear batch of cotton yarn to prevent uneven dyeing during use.